Do you have thinning hair, nails that break easily, or skin that never seems to be at its best? Zinc could be the missing element in your skincare routine. Essential for many functions in the body, zinc plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin, strong hair, and strong nails.
The importance of zinc
Zinc is an essential trace mineral that participates in many biochemical reactions in our bodies. It is vital for the optimal functioning of our immune system, tissue repair, cell growth, and plays an important role in protein synthesis and cell division. This mineral is particularly important for healthy hair, nails, and skin.
Fight against hair loss
A zinc deficiency can lead to hair loss because this mineral supports the growth and repair of hair tissue. Zinc helps maintain the function of the sebaceous glands that surround hair follicles, thus contributing to a healthy environment for hair growth.
Nail strengthening
Weak and brittle nails can also be a sign of zinc deficiency. Zinc is needed for protein synthesis, a process essential for nail growth and strength.
Skin improvement
Zinc also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can benefit the skin, especially in cases of acne or other skin conditions. By regulating sebum production and reducing inflammation, zinc can help reduce breakouts and promote clearer, healthier skin.
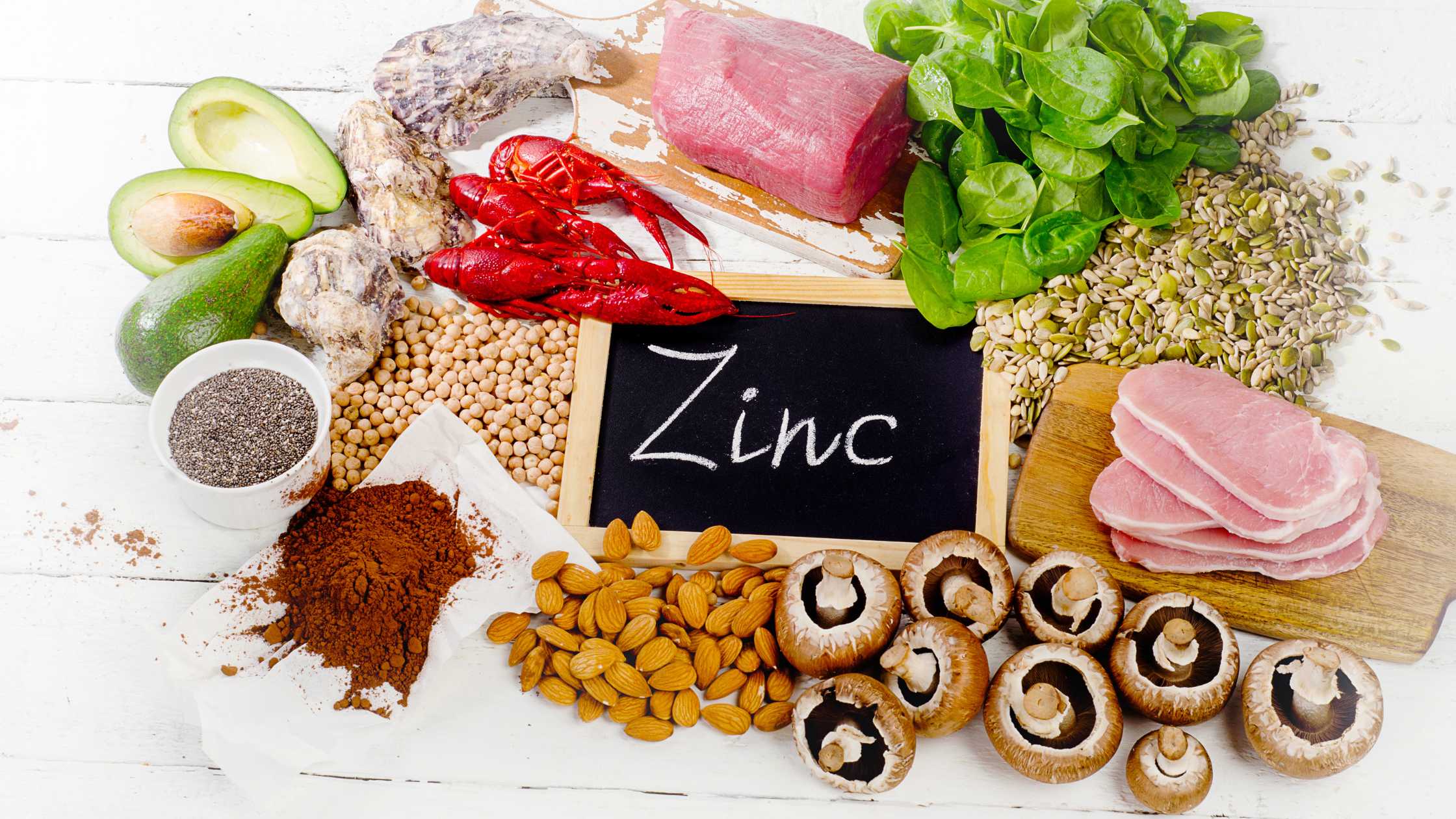
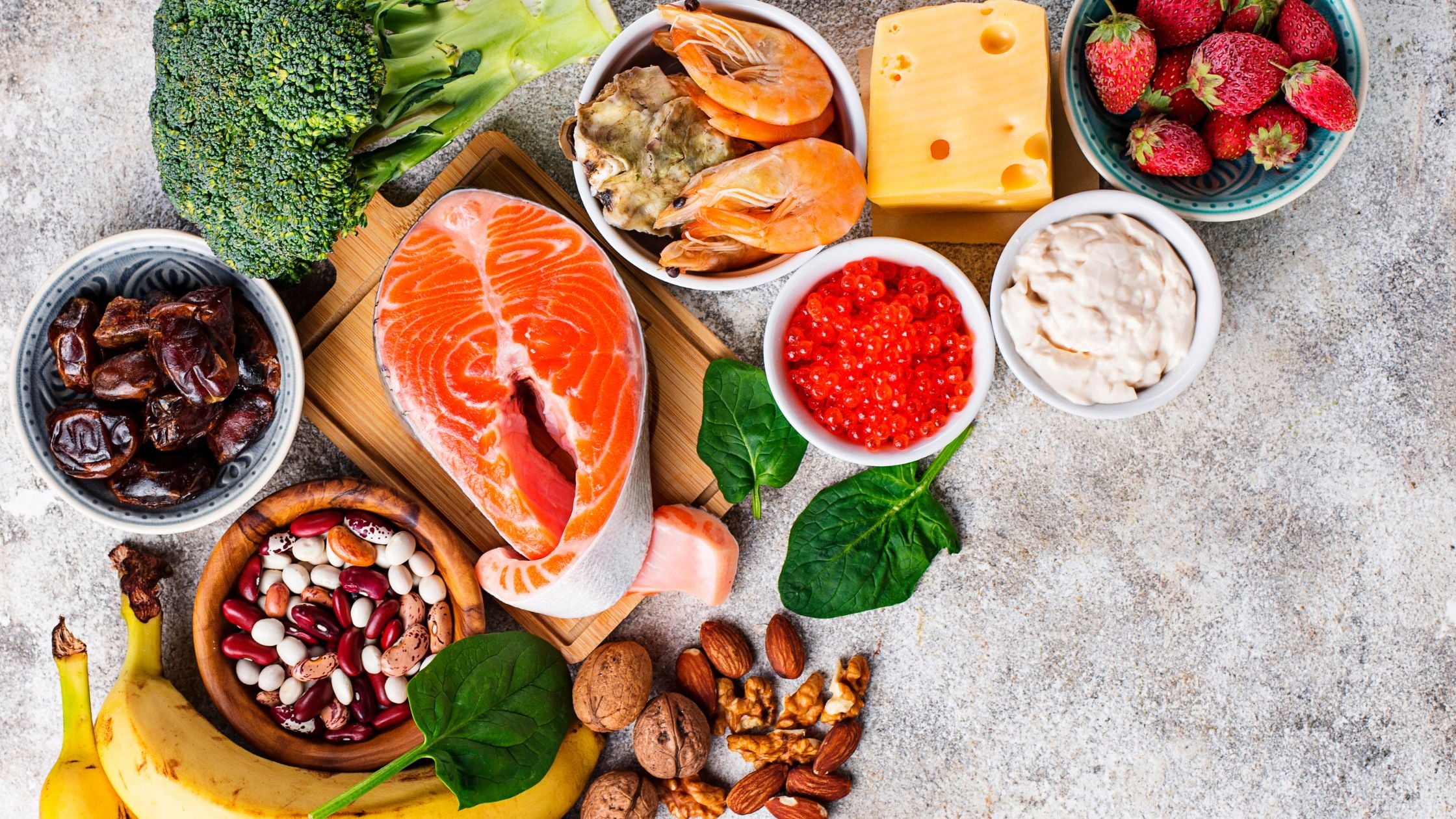
Food Sources of Zinc
To get more zinc into your diet, choose foods such as:
- red meat,
- seafood (especially oysters),
- legumes,
- nuts,
- the seeds
- and dairy products.
For those who have difficulty obtaining enough zinc from their diet, supplements may be considered, always under medical advice, such as the Magnesium-Zinc-L-theanine complex.
Read more

Let's talk about a topic that directly affects your well-being: micronutrients. These essential elements play a major role in our nutrition, energy, and overall health. Vitamins: Energy Boosters...

Summer is synonymous with sun, beaches, and tanned skin. However, preparing your skin for sun exposure and improving the quality of your tan requires more than just sunscreen. Did you know that a ...